Advance income, as the name suggests is said to be when the payment of income is made before its actual time. This advance income may sometimes be required by the sellers as safety against non-payment or to cover costs for supplying or providing goods or services.
For instance, consider the rent of a conference hall is Rs. 25,000 for a per-day seminar. The owner of the conference hall can demand to make an upfront payment of Rs. 10,000 or more or less depending on the need or situation or norms. This payment is just to ensure the booking status as confirmed. This upfront payment done by the receiver or the user is called an Advance Income.
In this blog, we will talk about GST on advance income.
GST on Advance Income
As per the GST law, the Goods and services tax in India is to be paid whenever there is supply of goods or services. Further, the time of supply determines the payment of GST. The general rule for time of supply is the earliest date of the following:
– Firstly, issue of invoice, or
– Secondly, receipt of payment/advance or
– Thirdly, date on which invoice should be issued
Also Read: Relevance of Supply under GST

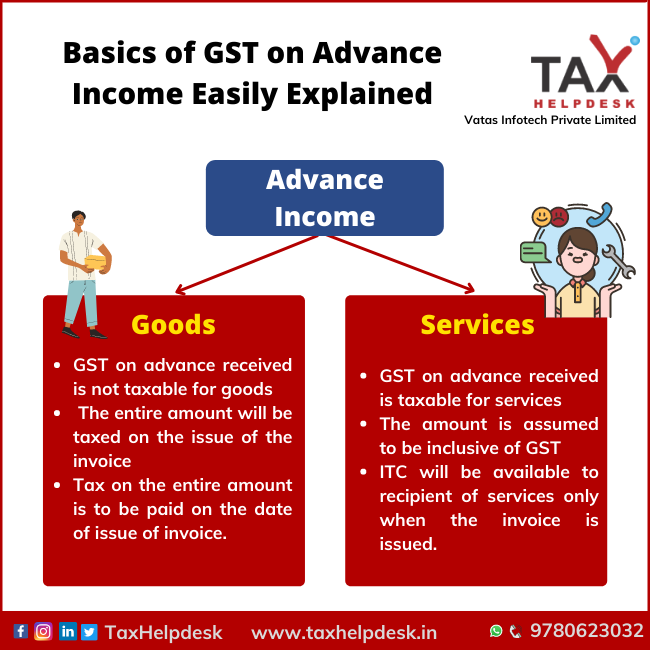
Taxability of Advance Payment received for goods and services
The GST taxability on advance income received for goods is different for services, which is as follows:
| Scenario | GST on Advance Income received for goods | GST on Advance Payment received for services |
|---|---|---|
| Taxability | GST on advance received is not taxable for goods | GST on advance received is taxable for services |
| Amount | The entire amount will be taxed on the issue of the invoice | The amount is assumed to be inclusive of GST |
| Invoice | Tax on the entire amount is to be paid on the date of issue of invoice. | ITC will be available to recipient of services only when the invoice is issued. |
Therefore, in case of services, if a supplier demands an advance payment before rendering them, GST has to be paid on advance amount even if service has not yet been rendered.
Note:
The advance income is not subject to GST for the registered person whose aggregate turnover in the preceding financial year have not exceeded Rs. 1.5 crores or likely to exceed Rs. 1.5 crore in the year of GST registration and who did not opt for the composition levy scheme. (Notification No. 40/2017–Central Tax dated 13th October, 2017)
Things to do: If registered person receives advance income
When a GST registered person receives advance income, he has do the following:
– Firstly, issue a GST Receipt Voucher
– Additionally, calculate the tax liability on Advance received
Issue a GST Receipt Voucher
After receiving the advance income, the supplier has to issue a GST receipt voucher to the person paying in advance. The receipt voucher will contain the following details:
– Firstly, the name, address and GST Identification number of the supplier of the goods or/and service;
– Secondly, the advance receipt voucher must contain a consecutive serial number not exceeding sixteen characters, containing alphabets or numerals or special characters;
– Thirdly, the date of issue;
– Fourthly, the name, address and Goods and services tax (GST) Identification Number, if registered, of the recipient;
– Fifthly, the details of goods or services;
– Amount of advance received;
– Sixthly, the rate of tax;
– Seventhly, the amount of tax charged in regard to taxable goods or services;
– Eighthly, the place of supply along with the name of State and its code
– Ninthly, whether the GST is payable under the reverse charge basis; and
– Lastly, the signature or digital signature of the supplier or his authorised representative.
Also Read: Qualifications for GST Registration
Calculate the tax liability on Advance received
After issuing the receipt voucher, the supplier needs to calculated tax liability on advance income and pay tax while filing GST Return for relevant month. While calculating the tax liability, the advance amount must be included in the amount. In addition to this, if the rate of the tax cannot be determined during receipt of advance GST, then GST @18% is to be charged. Also, if the point of sale cannot be ascertained, then advance is to be considered as interstate supply and accordingly, IGST is to be paid.
Treatment of Advance Income Received In GST Return
The amount received as advance income is required to be mentioned in Sr. No. 11A of the GSTR-1 Return. This serial number shows the figure of the advance money received in the tax period for which invoice has not been issued.
Additionally, it is important to note that in Sr. No. 11A of the GSTR – 1 Return figures of the advance money received must be bifurcated in two parts i.e.
– Advance income received against intra-state supplies and
– Advance income received against inter-state supplies.
However, consolidated figures of the advance money received are to be stated in the same, details of each advance money received need not to be mentioned.
The gross amount of advance income received is required to be mentioned under the head ‘Gross Advance Received / Adjusted’ and matching tax liability is required to be reflected under ‘Central’ and ‘State/ UT’ head in case of intra-state supplies and under ‘integrated’ head in case of inter-state supplies.
Also Read: Inspection, Search, Seizure & Arrest Under GST
If you still have doubts regarding GST on advance income, then leave a comment below or reach out to the TaxHelpdesk’s experts for GST consultation today. For more updates on Taxation, Financial and Legal matters, join our group on WhatsApp, channel on Telegram or follow us on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and Linkedin!
The views of the author are personal. TaxHelpdesk does not owe any responsibility towards anyone with regard to this blog!


Pingback: Basics of GST on Advance Income Easily Explaine...